Cush Clamps – What is It?
In piping and plumbing applications, we are using different kinds of systems and parts that have very important duties in these systems. One of these parts is the cush clamps. Here, we will take a look at the general important points about the cush clamps and their uses.
What are Cush Clamps?
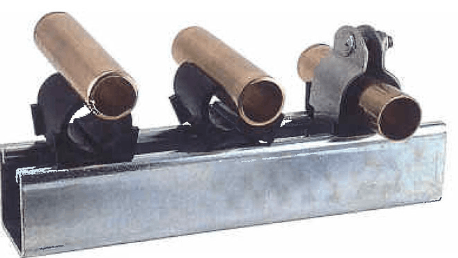
The name cush clamp comes from the cushion clamps that we are “cushioning” the pipe and plumbing connections and carriers. We are generally using a fastener or welded clamp applications in the pipe connections. And also for some applications, we are using them between the pipes and the clamps. They are polymer materials that provide very smooth and good vibration and sound absorption. So, their use is very common in plumbing applications.
Also, they provide very good sealing in the pipe connection sections. Because of these reasons we are using them in the piping and plumbing systems.
Their application of they is generally very easy. Operators are generally placing these round and polymer parts on the inside surface of the pipe clamps. And they pass the tubes and pipes through this structure. And they tighten the fasteners to obtain a strict pipe connection with a cush clamp.
Important Points about Cush Clamps
In general, you can find this information about them in the manufacturer’s catalogs.
- Nominal Pipe Size: The outside diameter of the pipe application that you will use the cush clamps. You need to select the cush clamp applications according to this value.
- Nominal Copper Water Pipe: Also, if you are looking for them for copper water pipe applications, you need to look for the diameter size of them.
- Steel Tube Size: This is the list that you need to look for the diameter of them.
Conclusion
As you see above, cush clamps are a very simple and basic but very important part of piping and plumbing applications. If you have additional comments and questions about this topic, please leave them below.
Also, you can find other useful and insightful articles about piping and HVAC on fmechanic.com!
Stainless Steel Heat Exchanger – Advantages and Types